Congo (DRC) Country Profile – Geography
Last update on: 3 June 2021

From Cia Factbook (Page last updated on October 06, 2020)
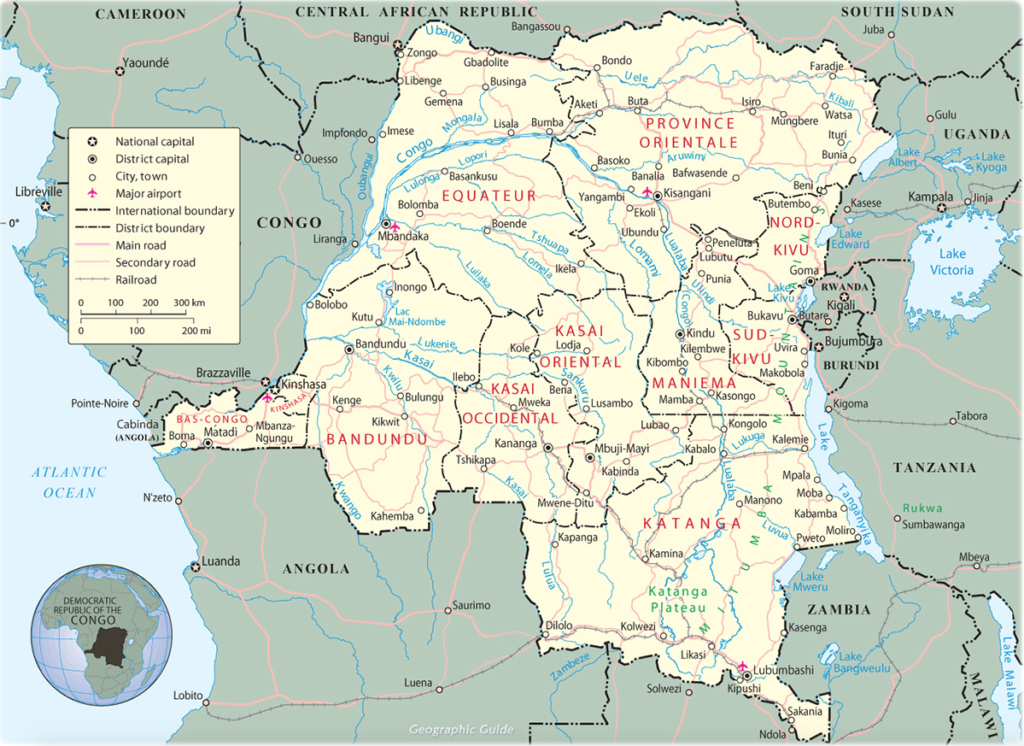
Location: Central Africa, northeast of Angola
Area:
- total: 2,344,858 sq km
- land: 2,267,048 sq km
- water: 77,810 sq km
Land boundaries:
- total: 10,481 km
- border countries (9): Angola 2646 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of Angola’s discontiguous Cabinda Province), Burundi 236 km, Central African Republic 1747 km, Republic of the Congo 1229 km, Rwanda 221 km, South Sudan 714 km, Tanzania 479 km, Uganda 877 km, Zambia 2332 km.
Coastline: 37 km
- territorial sea: 12 nm
- exclusive economic zone: since 2011 the DRC has a Common Interest Zone agreement with Angola for the mutual development of off-shore resources
Climate: tropical; hot and humid in equatorial river basin; cooler and drier in southern highlands; cooler and wetter in eastern highlands; north of Equator – wet season (April to October), dry season (December to February); south of Equator – wet season (November to March), dry season (April to October)
Terrain: vast central basin is a low-lying plateau; mountains in east
Elevation:
- mean elevation: 726 m
- lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- highest point: Pic Marguerite on Mont Ngaliema (Mount Stanley) 5,110 m
Natural resources: cobalt, copper, niobium, tantalum, petroleum, industrial and gem diamonds, gold, silver, zinc, manganese, tin, uranium, coal, hydropower, timber.
Land use:
- agricultural land: 11.4% (2011 est.) – arable land: 3.1% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.3% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 8% (2011 est.)
- forest: 67.9% (2011 est.)
- other: 20.7% (2011 est.)
Irrigated land: 110 sq km (2012)
Population distribution: urban clusters are spread throughout the country, particularly in the northeast along the boarder with Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi; the largest city is the capital, Kinshasha, located in the west along the Congo River; the south is least densely populated.
Natural hazards: periodic droughts in the south; Congo River floods (seasonal); active volcanoes in the east along the Great Rift Valley
volcanism: Nyiragongo (3,470 m), which erupted in 2002 and is experiencing ongoing activity, poses a major threat to the city of Goma, home to a quarter million people; the volcano produces unusually fast-moving lava, known to travel up to 100 km /hr; Nyiragongo has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth’s Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; its neighbor, Nyamuragira, which erupted in 2010, is Africa’s most active volcano; Visoke is the only other historically active volcano
Environment – current issues: poaching threatens wildlife populations; water pollution; deforestation (forests endangered by fires set to clean the land for agricultural purposes; forests also used as a source of fuel); soil erosion; mining (diamonds, gold, coltan – a mineral used in creating capacitors for electronic devices) causing environmental damage

These products are the results of academic research and intended for general information and awareness only. They include the best information publicly available at the time of publication. Routine efforts are made to update the materials; however, readers are encouraged to check the specific mission sites at https://monusco.unmissions.org/en or https://peacekeeping.un.org/en/mission/monusco.
Index
Executive Summary / Current Political and Security Dynamics / Recent Situation Updates
Congo Country Profile
Government/Politics /Geography / Military / Economy / Social / Information / Infrastructure
United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO)
Senior Leaders of the Mission / Mandate / Strength / Deployment of Forces / Casualties / Mission´s Political Activities / Security Council Reporting and Mandate Cycles / Background of Conflict / Timeline
